The Diverse Landscapes of Kurdistan
Kurdistan, often referred to as the "Land of the Kurds," is a geographically diverse region spanning parts of southeastern Turkey (Northern Kurdistan), northern Iraq (Southern Kurdistan), northwestern Iran (Eastern Kurdistan), and northern Syria (Western Kurdistan). This mountainous area covers approximately 450,000 square kilometers (174,000 sq mi) and is characterized by its rugged terrain, fertile valleys, and strategic location.
Key Geographical Features
- Mountains: Zagros and Taurus mountain ranges
- Rivers: Tigris, Euphrates, and their tributaries
- Climate: Varied, from Mediterranean to continental
- Natural Resources: Oil, water, and fertile agricultural land
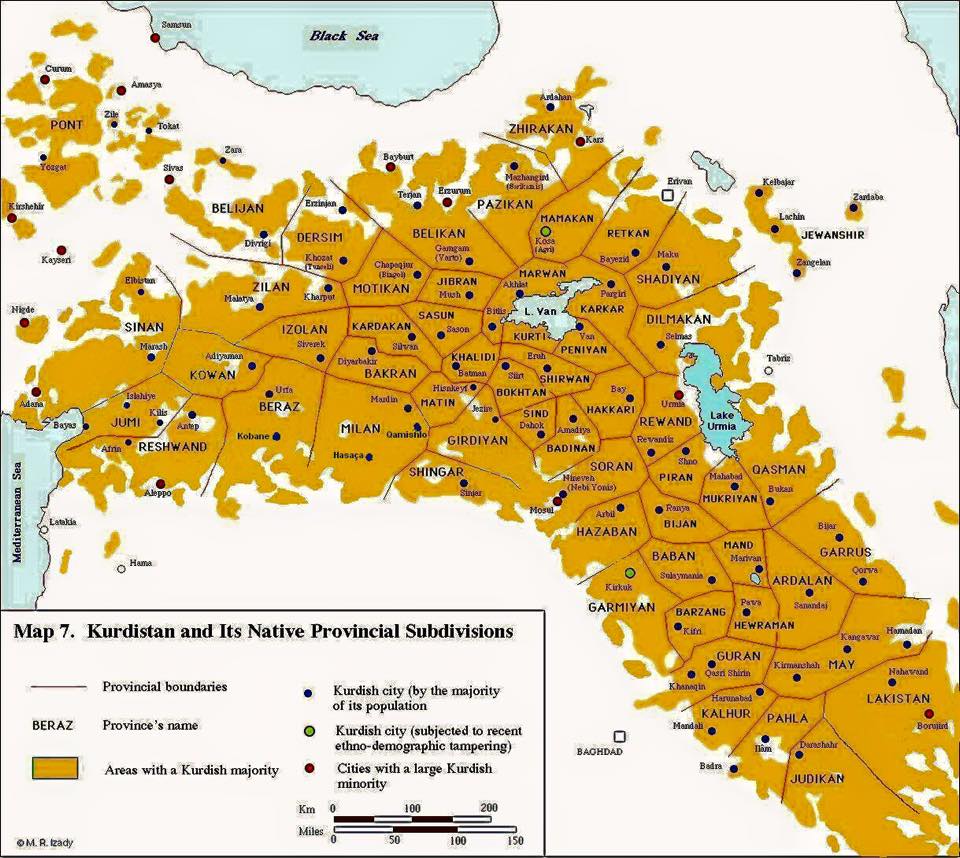
Map of Kurdistan
Topography
The topography of Kurdistan is dominated by the Zagros Mountains, which run from northwestern Iran through northern Iraq and into southeastern Turkey. These mountains, with peaks reaching over 4,000 meters (13,000 feet), have played a crucial role in shaping Kurdish culture and history, often providing natural fortifications and refuges.
Climate
The climate of Kurdistan varies significantly due to its diverse topography:
- Mediterranean climate in the west, with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters
- Continental climate in the interior, characterized by hot summers and cold winters
- Alpine climate in the high mountains, with snow-capped peaks year-round in some areas
Water Resources
Kurdistan is often called the "water tower" of the Middle East due to its abundance of freshwater resources. The region is the source of several major rivers, including:
- Tigris (Dicle in Kurdish)
- Euphrates (Firat in Kurdish)
- Great Zab
- Little Zab
These rivers and their tributaries are vital for agriculture, hydroelectric power, and water supply in the broader region.
Natural Resources
Kurdistan is rich in natural resources, particularly:
- Oil: Major oil fields in Kirkuk (Iraq) and around Qamishli (Syria)
- Natural gas: Significant reserves, especially in Iraqi Kurdistan
- Minerals: Including copper, gold, and iron ore
- Agricultural land: Fertile valleys suitable for various crops
Biodiversity
The varied landscapes of Kurdistan support a rich biodiversity, including:
- Flora: Oak forests, pistachio trees, and diverse alpine vegetation
- Fauna: Persian leopards, Syrian brown bears, and numerous bird species
Landscape Gallery






Environmental Challenges
Despite its natural wealth, Kurdistan faces several environmental challenges:
- Deforestation due to overgrazing and urbanization
- Water scarcity and management issues, exacerbated by climate change
- Air and water pollution from oil extraction and processing
- Soil erosion in agricultural areas
Geography and Kurdish Identity
The geography of Kurdistan has played a significant role in shaping Kurdish identity and culture. The mountainous terrain has historically provided protection and fostered a strong sense of independence. Today, the management and distribution of natural resources, particularly water and oil, continue to be central issues in the political discourse surrounding Kurdish autonomy and relations with neighboring states.



